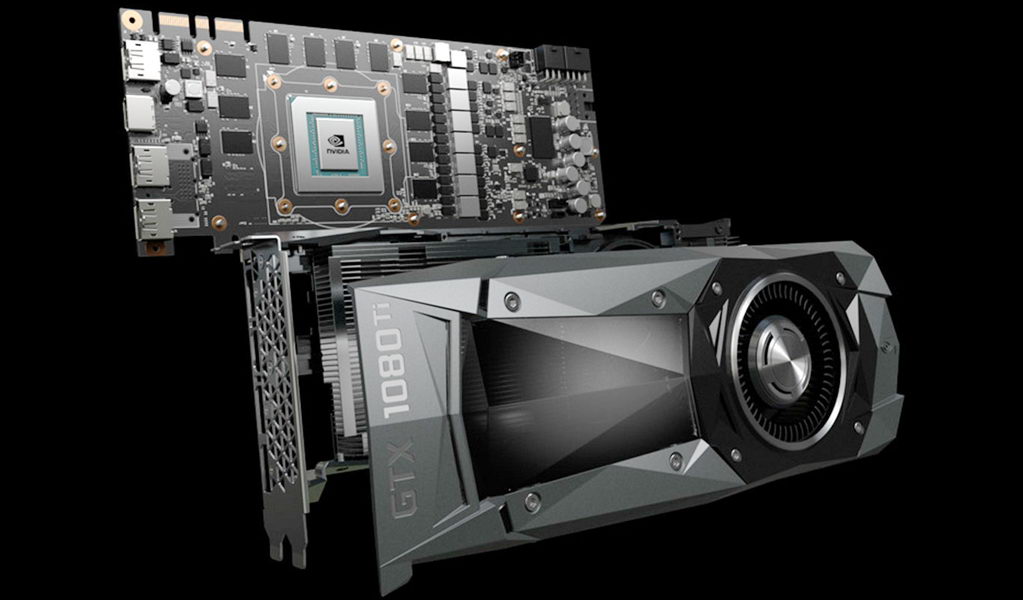
by CDO Technolgy | Jun 25, 2017 | CDO Technology News, Gaming System, Pro Workstations
When determining which kind of graphics card would be ideal for a particular computer system, one must consider for what purpose the system is to be used. There are two primary classifications of graphics cards: professional and consumer. The professional cards are optimized for productivity applications, while the consumer cards are optimized for recreation and entertainment purposes. Two of the most commonly sought after professional graphics cards are the NVIDIA Quadro and the AMD FirePro. Quadros come in several varieties, with a range that encompasses an astonishing array of different types. Each type has its own combination of possible factors, including speed, memory, power usage, and connector. AMD’s FirePro also represents a fairly large range of possibilities and options to enhance compatibility, however this company tends to have a rather small share of the overall graphics card market. Still, the FirePro is a powerful graphics card made to run efficiently with a reasonable power draw.
The main pros for professional graphics cards include excellent performance, especially for CAD programs and similar productivity software, products for mobile devices, continuing innovation, and specialized technology. Professional graphic cards also have stricter quality control and use better parts in manufacturing and are designed to run 24/7 at peak workload. Their software (drivers) have been tested/certified to work with professional applications while consumer grade has not.
Cons include a higher price, the need to examine the specifications carefully to be sure the correct one has been chosen for the machine into which it is to be installed, and the fact that some need additional cables or adapters that may or may not be included in the package.
Common consumer graphics cards include the NVIDIA GeForce and the AMD Radeon. NVIDIA’s GeForce has at least 13 series, each a bit better than the last. They also have options for mobile devices and smaller machines. These graphics cards are well known among gamers as an excellent option. The newest series, GTX, takes gaming to a new level with Maxwell architecture for acceleration, offering fast performance and the latest technology for gaming. AMD’s Radeon is geared for speed, immersion, and graphics that dazzle the eyes. Their processors are optimized for efficiency of power while delivering a visual experience that more than satisfies.
These consumer graphics cards’ upsides include the fact that they are specifically geared to gaming, allowing quick drawing for higher frame rates. They contribute to lower latency and better visuals. The downsides of these cards include the fact that, generally, they use quite a bit of power. They tend to heat up quickly and, without proper ventilation, can overheat. They are one of the largest components you may add to your computer, when upgrading.
When choosing a graphics card for a system, lean strongly toward a professional graphics card if the machine is to be used for CAD or other design-oriented software. Choose a consumer graphics card if the machine is intended for gaming.
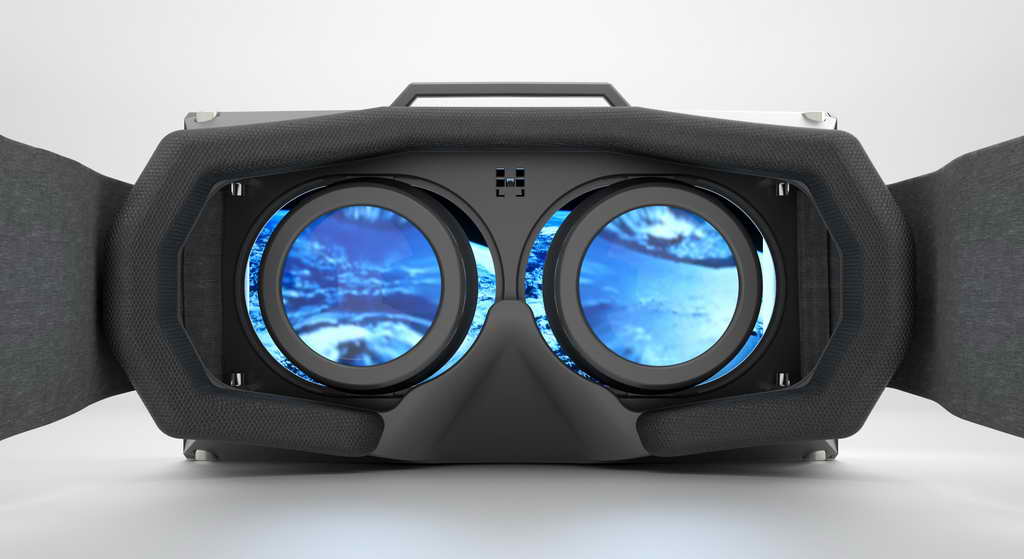

by CDO Technolgy | Feb 2, 2016 | CDO Technology News, Gaming System, Virtual Reality
For gamers and tech-addicts, 2016 is shaping up to be a storm of incredible leaps forward in virtual reality technology. Although many consoles are taunting potential virtual reality players with cheap models, those who want the full experience know that a spec’d-out PC is a must for the full experience.
Building a VR-ready PC for the Oculus Rift might seem intimidating and expensive at first, but with our guide, you can get in on the fun with any budget:
Important Components:
GPU: Your graphics-processing unit will make or break your VR experience. To sustain the 90FPS world of VR gaming, you need a GPU that won’t slow down at crucial times. Rift developers recommend running either the NVIDIA GTX 970 or AMD R9 390 when using the Oculus Rift.
RAM: Normally, you want a minimum of 8GB onboard ram for optimal game performance. This spec holds true when building a VR-ready console, but investing in an upgrade to 16GBs of onboard ram will guarantee your machine runs smoothly.
CPU: The slowest processor that can get the job done is the Intel i5-4590, or another power-equivalent CPU. Overall, your build can get away with running on a lower-end CPU, as long as you account for potential bottlenecking. Only consumers looking to build a high-end VR machine will warrant investing in an expensive CPU.
Motherboard: Although the motherboard doesn’t directly affect your VR experience, it provides the backbone for the rest of your hardware. Be sure to check the compatibility of any motherboard you are considering with the additional components of your build. Finding a motherboard that supports USB 3.0 is highly recommended.
PSU: When choosing your power supply unit, it’s best to plan ahead. VR setups run power usage-heavy peripherals, and you want to ensure the high-end graphic cards you upgrade to in the future will run properly. Having a PSU powerful enough to prevent immersion-breaking fan-noise is a must.
Storage: Running either a SSD or HDD will work when building a VR-ready PC. However, an investment in an SSD will speed up game performance, keeping you fully immersed in your VR worlds.
Recommended Specs:
Official Oculus Minimum Specs:
- CPU: Intel Core i5-6500 equivalent or greater
- GPU: NVIDIA GTX 970 / AMD 290 equivalent or greater
- RAM: 8GB+ RAM
- 2x USB 3.0 ports
- Windows 7 SP1 or newer
- Compatible HDMI 1.3 video output
Solid Specs:
- CPU:Intel Core i5-6500
- GPU:GeForce GTX 980 or Radeon R9 390X
- Storage 1:128 GB SSD
- Storage 2:1TB HDD
- RAM:8GB DDR4
Mid-Range:
- CPU:Intel Core i5-6600K
- GPU:GTX 980 Ti
- Storage 1:250GB SSD
- Storage 2:2TB SATA HDD
- RAM:16GB DDR4
High-End:
- CPU:Intel Core i7-6700K
- GPU:GTX 980 Ti (alternative: 2x GTX 980 Ti)
- Storage 1:512GB Samsung 950 Pro PCIe M.2 SSD
- Storage 2:4TB HDD
- RAM:16GB DDR4

by CDO Technolgy | Mar 12, 2015 | CDO Technology News, Gaming System
Game Enthusiasts understand that no other platform can match the quality and intensity of the game-play that you can get from a correctly configured Gaming Desktop. These Game Enthusiast Desktops are very specialized high-performance systems where choosing the right components really does matter. If you want to play the most current, intensive, and demanding games you will need to be sure you pick the correct processor, quantity of RAM, hard drive, and of course, GPU (graphics processing unit).
Today’s Gaming Desktop market has many choices. Such as: standard, overclocked and liquid-cooled CPUs, mid to high end graphic cards, multi-graphic card(s) choices for Crossfire and SLI, many different options for RAM, and mechanical HDDs & SSD drive choices. The following is some of the information you will need to correctly customize a good Gaming Desktop.
Processor (CPU)
A solid starting point good Gaming Desktop is quad-core processor. Manipulating and creating 3D objects for the complex games of today requires high frequency CPUs. Systems that have safely overclocked processors can provide up to 25% more CPU frequency for games than standard CPUs. Liquid cooling systems can help to keep the CPU cool when the processor is stressed.
GPU / Graphics/Video Card
The GPU (graphics processing unit) is the processor on the graphics card. It creates the image you see on your LCD monitor. You want the GPU to be able to squeeze the highest number of frames per second out of your gaming system. Playing the most demanding games with the graphics set to the highest resolution and a high frame-rate, will require a high-performance graphics card. If you are running a single 1920 x 1080 monitor, buy the best single graphics card you can afford.
Large & High Resolution Display Screens (Monitor)
A high resolution display requires a lot of GPU memory and that is only available on top end cards. When running high monitor resolutions and 4K displays, multi-graphics cards are a good idea. While adding a second graphics card won’t double the performance; you will typically see a 25-50% increase. Multi-graphic card setups tend to consume a lot of power and can generate a lot of noise, but for those that want the biggest, badest gaming PC on the block, it will be well worth it.
RAM / System Memory
Having enough RAM is always important. It is better to have more memory than not enough. Sometimes it is difficult to determine how much is adequate. More RAM will allow you to do more multitasking without getting bogged down. We recommend at least 8GB of RAM as a minimum to start with and much more for demanding games. A good rule of thumb is having as least a 25% buffer of RAM usage while running very intensive games.
Hard Drives (HDD vs SSD)
The types of hard drive that are most commonly used are the disk based SATA HDD (hard disk drive) and the chip based SSD (solid state drive). By using SSDs you will have increased data read times and decreased seek times versus SATA HDD drives. Sustained read times can also be more than four to five times higher with an SSD as well, seek times are also much faster. Consequently you will see that SSDs, being faster, are rated in nanoseconds instead of milliseconds like SATA drives. Using SSD’s can cause system performance to increase dramatically. For good balance that utilizes the strengths of both technologies we recommended using at least a 250GB SSD is for the O/S and program installation and also 1TB to 3TB SATA mechanical drive for data storage. For extreme performance you should consider using a striped RAID; check out our RAID article for more information.



