What is a Server? Computer Network Servers Explained.
What are Servers?
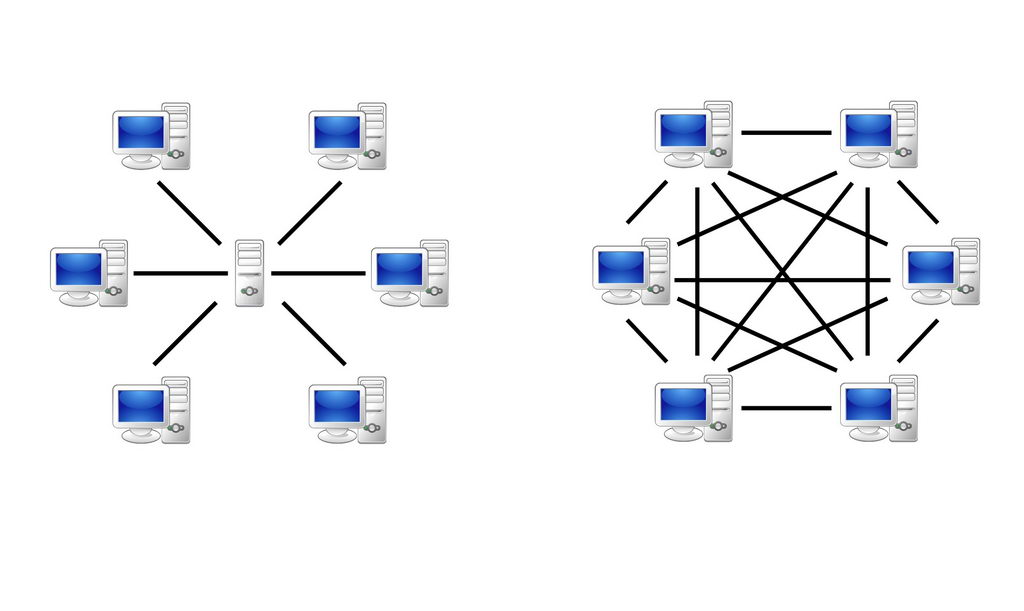
Servers have been around as long as networks. The generic use of a server is to ‘serve’ something to other computers. This communication is done with a variety of different server types with their own specific uses. They act as facilitators, storage, and so on. Not all server types are exclusive; many types can be simultaneously in use on the same server machine. Some servers can even be client computers (those on which people access the data being served) at the same time.
Some common types of servers are most recognizable. These are: FTP, proxy, game, and web servers. These machines are usually somewhat similar to the personal computers found in most homes and businesses, although they usually have specific software and hardware to provide a smoother transition of the data. Servers usually have more storage space, faster processors, and more RAM (random access memory) in order to make them more efficient. Rather than a standard operating system used by the general public (such as Windows 7), servers usually have a server platform. An example of this for a PC would be Microsoft Server.
FTP servers are used to provide access to files, either publicly or after using a login, depending on whether the files are free or for a fee. This functionality is usually included on web servers, as well, to allow easy access to web site owners to upload and download their own files.
Proxy servers are an extra step between the end user (also known as the client computer) and another server (usually a web server) that handles filtering, sharing connections, and helps to improve performance. These are sometimes used by employers to limit employees’ access to certain web sites from the workplace.
Game servers are those used by online games to provide the interface and processing for them. These are most notable when the game is an MMO (massive multiplayer online) game, in which many people around the world are connecting at the same time, to play the same game. There is often interaction between the players, which necessitates a server that is powerful enough to keep up without causing lag (pauses in the gameplay, during which the game continues, but the player misses the action because the server ‘catches them up’ by skipping).
Web servers are by far the most common ones. These are the servers that house the web pages (such as the one you are currently reading). These communicate with the client’s browser and send the information – text, images, videos, etc. – that is requested. Pretty much anything that is accessed through a browser (such as Internet Explorer, Firefox, Chrome, etc.) is processed by a web server.
Others include application servers, which handle linking databases with web servers; list servers, which handle mailing lists for newsletters and other bulk email processes; chat and IRC (internet relay chat) servers, which allow real-time communication between people wherever they are; mail servers which handle basic email; and news servers which carry newsgroups such as the USENET service, although these are not as popular among the general public as they once were.